Driven Development
- 6 mins
As i would like to describe it driven development is the twist between developers and business guys that makes them survive together to translate the requirements into a software features in an organized flow.
TDD
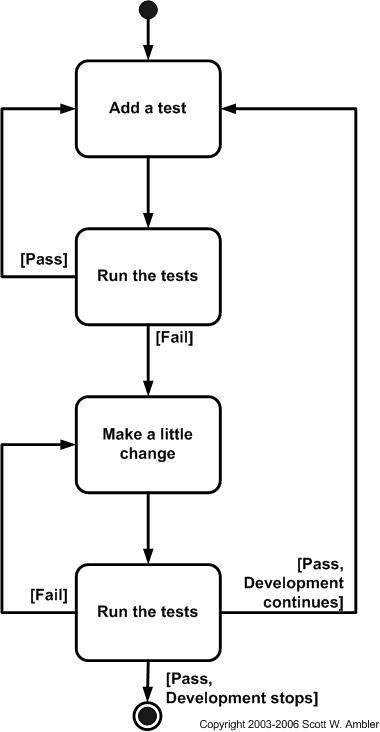
a short for test-driven-development, TDD can be defined as a programming practice that instructs developers to write new code only if an automated test has failed. This avoids duplication of code. TDD means "Test Driven Development". The primary goal of TDD is to make the code clearer, simple and bug-free.follow the diagram to understand the flow of tdd.
Advantages of TDD
- Early bug notification.
- Better Designed, cleaner and more extensible code.
- Confidence to Refactor
BDD

a short for Behavior-driven-development, BDD lets us develop, test and think about the code from the view of the business owner.
characteristics
- tests are writen ahead of the code like tdd.
- tests are more user-focused and based on the system’s behavior.
Essentials to have in place before implementing BDD
- Requirements should be converted into user stories that can define concrete examples.
- Each example should be a valid user scenario, rather than a mere test case.
- An understanding of the role-feature-reason matrix and the given-when-then formula.
- An awareness of the need to write ‘the specification of the behavior of a class’ rather than ‘the unit test of a class’.
Templates for writing BDD
The ‘Given-When-Then’ formula BDD example
Given a certain scenario
When an action takes place
Then this should be the outcome.
Example
Role-Feature-Reason matrix
This template is also used in BDD, in order to aid user story creation. This template is defined as:-
As a
I want
So that
An example of such a user story would be:
As a retail customer,
I want to return an electronically purchase merchandise within 14 days, so that the refund will be processed
benefits to using BDD
- You are no longer defining ‘test’, but are defining ‘behavior’.
- Better communication between developers, testers and product owners.
- Because BDD is explained using simple language, the learning curve will be much shorter.
- Being non-technical in nature, it can reach a wider audience.
- The behavioral approach defines acceptance criteria prior to development.
TDD VS BDD
Behavior vs Test
In TDD I don’t care much about the output. The only thing needed is to carry out the test in a particular way.
But in BDD I don’t mind how you come up with the output, only that the output has to be correct under the GIVEN condition.
Communication and feedback
In BDD you will come across a better specification since communication between the software developer and product owner is fast and easy.
TDD may lack the ability to specify the exact behavior, but you achieve higher quality with software code.
Writing Failing Tests vs Writing Failing Feature Tests.
In BDD, a test is written that can satisfy both the developer and customer, but in TDD you write a test that will only satisfy a developer and the code they write. As can be seen below.
DDD

a short for Domain-driven-development,DDD is a software development approach that uses and builds upon OOP(object opiented programming) principles and ideas, and now we have to ask two important questions.
What is the Domain?
The common dictionary definition of domain is: “A sphere of knowledge or activity.”
Domain in the realm of software engineering commonly refers to the subject area on which the application is intended to apply. In other words, during application development, the domain is the sphere of knowledge and activity around which the application logic revolves.
What is Domain-Driven Design?
is the expansion upon and application of the domain concept, as it applies to the development of software. It aims to ease the creation of complex applications by connecting the related pieces of the software into an ever-evolving model.
DDD focuses on three core principles:
- Focus on the core domain and domain logic ( business logic ).
- Base complex designs on models of the domain.
- Constantly collaborate with domain experts, in order to improve the application model and resolve any emerging domain-related issues.
Building Blocks of DDD
Domain-driven design also defines a number of high-level concepts that can be used in conjunction with one another to create and modify domain models:
Entity
An object that is identified by its consistent thread of continuity, as opposed to traditional objects, which are defined by their attributes.
Value Object
An immutable (unchangeable) object that has attributes, but no distinct identity.
Domain Event
An object that is used to record a discrete event related to model activity within the system. While all events within the system could be tracked, a domain event is only created for event types which the domain experts care about.
Aggregate
A cluster of entities and value objects with defined boundaries around the group. Rather than allowing every single entity or value object to perform all actions on its own, the collective aggregate of items is assigned a singular aggregate root item. Now, external objects no longer have direct access to every individual entity or value object within the aggregate, but instead only have access to the single aggregate root item, and use that to pass along instructions to the group as a whole. This practice correlates with many of the actual coding practices we’re covering in our design patterns series.
Service
Essentially, a service is an operation or form of business logic that doesn’t naturally fit within the realm of objects. In other words, if some functionality must exist, but it cannot be related to an entity or value object, it’s probably a service.
Repositories
Not be confused with common version control repositories, the DDD meaning of a repository, repository is a service that uses a global interface to provide access to all entities and value objects that are within a particular aggregate collection. Methods should be defined to allow for creation, modification, and deletion of objects within the aggregate. However, by using this repository service to make data queries, the goal is to remove such data query capabilities from within the business logic of object models.
Factories
As we’ve discussed through a number of design patterns articles already, DDD suggests the use of a factory, which encapsulates the logic of creating complex objects and aggregates, ensuring that the client has no knowledge of the inner-workings of object manipulation.
Domain-driven design also heavily emphasizes the ever-more-popular practice of continuous integration
Summery
- TDD is a process of modifying the code in order to pass a test designed previously.
- BDD lets us develop, test and think about the code from the view of the business owner.
- DDD Focuses on the features in domain of our application this domain is defined by the bussiness logic.